Urobilinogen
Urobilinogen is a degradation product of conjugated bilirubin. Bilirubin is eliminated in the intestine with the bile. Bilirubin is metabolized into urobilinogen by bacteria in the colon, and eliminated in the feces. A small fraction is reabsorbed into the bloodstream and is excreted by the kidneys. The presence of urobilinogen in urine depends on the permeability of the biliary tract, the intestinal reabsorption and liver and kidney function.
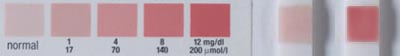
Test strip, from left to right: comparison scale, then a normal result, then a positive result (8-12 mg/dl).
Clinical relevance
Urobilinogen is absent in urine when bilirubin is not secreted in the intestine, for instance in case of hepatic failure or biliary tract occlusion.
Urinary urobilinogen is increased in cases of increased hemoglobin degradation, i.e. in hemolytic anemia.
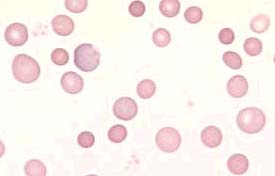
Blood smear: autoimmune hemolytic anemia with anysocytosis, poychromasia and spherocytosis